Vitiligo is a chronic autoimmune disease of multifactorial nature that causes skin depigmentation as a consequence of melanocyte loss. Although sometimes it is said to be untreatable, there are therapies that have succeeded in halting its progression and promoting repigmentation. One of these are inhibitors of the JAK-STAT pathway, which plays a prominent role in the immunopathogenesis of the disease. Ruxolitinib, a JAK 1/2 inhibitor, has been the first topical drug approved for the treatment of vitiligo. This narrative review addresses the immunopathologic processes involved in vitiligo, the role of the JAK-STAT pathway, and the efficacy and safety results of ruxolitinib in the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo in adult and adolescent patients older than 12 years with facial involvement. In addition, the psychological repercussions and the impact on the quality of life suffered by patients with vitiligo are described.
Vitiligo is an acquired, chronic disorder of skin pigmentation characterized by the presence of white patches.1–4 It can be of two types: non-segmental (the most common form, with symmetrical bilateral distribution) or segmental (less common, with unilateral distribution).1,5,6 Its prevalence is 0.5–2% and it affects men and women equally.6–8
Its etiopathogenesis is multifactorial, in which genetic susceptibility, changes in immune responses, and environmental triggers lead to oxidative stress.6,9–11 In segmental vitiligo, a neural hypothesis has been proposed.12 Multiple variants of genes involved in melanocyte biology, immune regulation, and apoptosis have been identified. Some of these genes include FOXD3, NLRP1, PTPN22, PDGFRA, HLA, and XBP1, among others.9,13,14 A certain degree of familial association has also been reported (approximately 20–30%), with a 6% risk in siblings and a 23% risk in monozygotic twins.9,13,14 A recent study explored the possible involvement of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) in skin affected by segmental vitiligo, detecting viral particles and compatible morphological changes in depigmented areas.15 These findings raise the possibility of viral participation in the initiation or progression of segmental vitiligo.
The most widely used treatments for vitiligo include topical corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus), particularly for localized lesions and sensitive areas such as the face and folds. In more extensive or refractory cases, narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy (NB-UVB) is used.16,17 More recently, inhibitors of the JAK–STAT pathway – directly involved in the immunopathogenesis of the disease – have shown promising results in skin repigmentation.18–20 Based on efficacy and safety results from phase III clinical trials, ruxolitinib cream was recently been approved for non-segmental vitiligo in adult and adolescent patients aged ≥12 years with facial involvement.21 This new topical therapy represents an advance over existing treatments for several reasons: it has a specific mechanism of action targeting the pathway directly involved in inflammation and melanocyte destruction in vitiligo (in contrast to the broader immunosuppressive effects of corticosteroids and tacrolimus); it has a better long-term safety profile (especially vs the systemic adverse effects of oral therapies or the local adverse effects of corticosteroids); it has demonstrated efficacy in achieving sustained repigmentation rates (particularly when combined with NB-UVB or in patients who did not respond to other topicals such as tacrolimus); and it has been specifically approved for vitiligo (as opposed to the off-label use of corticosteroids or tacrolimus).21–26Table 1 illustrates a comparative summary of the main treatments for vitiligo.
Comparison of the main topical treatments for vitiligo.
| Characteristics | Ruxolitinib cream21–26 | Tacrolimus88–90 | Topical corticosteroids88,91,92 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of action | Selective JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor | Calcineurin inhibitor (reduces IL-2 and other cytokines) | Non-selective immunosuppression (anti-inflammatory) |
| Efficacy (repigmentation) | High, especially when combined with NB-UVB | Moderate-high, especially on face and neck | High in the short term, but with relapse risk |
| Specific approval for vitiligo | Yes | No (off-label use) | No (off-label use) |
| Tolerance in sensitive areas (face/flexures) | Very good, with low risk of local adverse effects | Good, although it may cause initial irritation | Limited, with risk of atrophy and telangiectasias |
| Local side effects | Mild erythema, occasional pruritus | Burning or stinging initially | Skin atrophy, striae, telangiectasias |
| Systemic side effects | Very low risk (minimal absorption) | Low risk | Risk of hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis suppression if overused |
| Long-term use (>6 months) | Safe and well tolerated | Relatively safe but may cause irritation | Discouraged due to long-term adverse effects |
| Frequent combination with phototherapy (NB-UVB) | Yes, improves efficacy without increasing adverse effects | Yes, common in clinical practice | Yes, but with caution due to local adverse effects |
NB-UVB: narrowband ultraviolet B.
This article provides a concise review of the immunopathological processes involved in the onset and persistence of vitiligo lesions, focusing on the role of the JAK-STAT pathway, the role of inhibitors of this pathway in the treatment of the disease, and the safety and efficacy results from the phase III and extension studies of ruxolitinib cream. The psychological implications and the quality-of-life impact of vitiligo are also reviewed, as well as how early intervention can help improve these aspects.
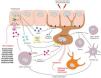
Immunopathology of vitiligoThe pathogenesis of vitiligo can be structured into three processes: initiation of the immune inflammatory response, progression and amplification of that response, and persistence or recurrence of vitiligo lesions. In all of these, the JAK–STAT pathway plays a fundamental role.6,9,20,27–37Fig. 1 and Table 2 illustrate the most important events occurring during these processes.6,9,20,27–37
Main molecular and cellular pathways leading to melanocyte detachment and the mechanism of action of several JAK inhibitors. CXCR3/CXCR3B: receptors for CXCL9/10; IFN-γ: interferon gamma; IFN-γR: interferon gamma receptor; MMP9: matrix metalloproteinase 9; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha.
Events occurring during the initiation, progression, and persistence of vitiligo.
| Initiation1. Melanocyte stress and activation of the innate immune response.6,27–292. Stimulation of melanocyte-specific CD8+ T cells and IFN-γ release.27–29 |
| Progression3. Initiation of the inflammatory IFN-γ – JAK1/2 – STAT1 – CXCL9/10 pathway.6,9,20,29–314. Recruitment of CD8+ T cells to the epidermis via the CXCR3 receptor.6,9,20,29,305. Progressive loss of melanocytes.6,9,20,29,306. Positive feedback loop (via CD8+ T cells, step 3).6,9,20,29,30 |
| Persistence or recurrence7. Persistence of disease due to IL-15 – JAK1/3 – STAT5 pathway signaling in tissue-resident memory cells.6,29,32–368. Persistent loss of melanocytes.6,29,32–36 |
The initiation phase occurs due to melanocyte stress and activation of the innate immune response.6,27–37 Melanocytes in patients with vitiligo display genetic and mitochondrial alterations that make them more susceptible to stress.6,27 Stressed melanocytes release exosomes containing pro-inflammatory mediators that activate innate immune cells such as dendritic cells, NK cells, and type 1 innate lymphoid cells.27,28,38 Activation of dendritic cells promotes antigen presentation to cytotoxic CD8 T cells, activating them against melanocytes and leading to IFN-γ release (Fig. 1).20,27,28,38 Meanwhile, keratinocytes display a heterogeneous organization of the actin cytoskeleton and E-cadherin, increased TNF-α, CXCL9/CXCL10 and IL-1, enlarged mitochondria, increased reactive oxygen species, and reduced antioxidants.6 Overall, these changes increase oxidative stress, favoring apoptosis and initiating the inflammatory reaction.6
Through the JAK-STAT pathway, there is increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9), which may cleave E-cadherin (anchoring melanocytes to the basement membrane), leading to melanocyte detachment and apoptosis (Fig. 1).27,39 House dust mites may also induce MMP9 expression, producing the same effect.40 Melanocyte detachment then increases apoptosis.
ProgressionOnce the inflammatory process has begun, amplification occurs. From keratinocyte STAT1, CXCL9 and CXCL10 are expressed. These chemokines act on melanocytes via the CXCR3B receptor and on T lymphocytes via the CXCR3 receptor (Fig. 1).6
CXCR3B expression plays a key role in melanocyte apoptosis.41 Activation of CXCR3B by CXCL10 on cultured human melanocytes induces apoptosis,41 intracutaneous CXCL10 levels can predict the inflammatory response,42 and increased numbers of CXCR3B+ melanocytes have been found in non-lesional vitiligo skin vs healthy skin.41
Through the CXCR3 receptor, CD8 T-cell recruitment occurs, also promoting melanocyte destruction.41 These lymphocytes produce IFN-γ, which binds to keratinocyte receptors, activating the JAK–STAT signaling pathway.27,28,38 This regulates production of CXCL9 and CXCL10, which in turn recruit more CD8+ T cells, creating a positive feedback loop resulting in widespread melanocyte destruction and depigmentation.27,28,38 Furthermore, IFN-γ activates melanocytes to express CXCR3, allowing CXCL9/10 to act directly on melanocytes (Fig. 1).20
During progression, MMP9 is produced via the JAK–STAT pathway, cleaving E-cadherin and favoring melanocyte detachment and apoptosis (Fig. 1).27,28
Persistence or recurrenceTissue-resident memory T cells (TRM) seem to play an important role in the persistence, maintenance, or recurrence of vitiligo lesions by reactivating an immune response vs any melanocyte entering the depigmented area.27,28,38,43 TRM cells depend on IL-15 signaling. Once IL-15 binds to its receptors, TRM cells activate JAK–STAT signaling, leading to activation of inactive memory T cells and recruitment and proliferation of CD8+ T cells in the skin. Through granzyme B or perforin, these cells cause melanocyte destruction and skin depigmentation.9,20,43
Integrating JAK inhibitors in the treatment of vitiligoEarly detection of vitiligo is essential for optimal treatment.16 Management requires a thorough initial evaluation to determine disease severity, extent, and individual prognostic factors.3,44 If there are signs of rapid progression, aggressive treatment should be considered to avoid irreversible damage to pigment cells and improve prognosis.44
However, according to data from the Global VALIANT study conducted in several EU countries, 65% of patients had been told that their vitiligo could not be treated, and consequently, 48% stopped seeking treatment.45
Treatment goals for vitiligo are well defined: halting disease progression, promoting repigmentation, and preventing relapse.46,47 In line with these goals, the international consensus on the diagnosis and management of vitiligo recommends topical therapy (with corticosteroids or immunomodulators), phototherapy, and/or systemic treatment for rapidly progressive vitiligo. In all cases, therapeutic decisions should be made in agreement with the patient, based on the course of the disease and individual burden.16
Halting disease progressionAlthough the clinical progression of non-segmental vitiligo is unpredictable, it generally presents with abrupt onset, rapid progression, and a period of stability.2 It shows a bimodal onset pattern: in some patients it begins during the early years of life (early prepubertal onset), while in others it begins later (late postpubertal onset).2,48–50 Early onset is usually associated with a higher genetic load and more extensive lesions. Late onset (3rd or 4th decades of life) generally shows a lower genetic burden and a smaller area of skin involvement.50–52 In all cases, when vitiligo is active, treatment should be initiated as early as possible.53
Treatment of active vitiligo includes oral corticosteroid minipulse therapy (5mg/kg of prednisolone on 2 consecutive days per week for three months, or 4mg of dexamethasone on 2 consecutive days per week); NB-UVB phototherapy 2–3 times per week for 3 months; or the combination of NB-UVB plus oral corticosteroid minipulse therapy (for highly active forms of the disease).17,54 Other drugs used include methotrexate, cyclosporine, and minocycline, although with lower levels of scientific evidence.
Several studies have compared corticosteroid minipulses with the combination of minipulses plus NB-UVB. The combination was found to be the most effective strategy for stopping disease progression, offering up to a 40% improvement over corticosteroid minipulses alone, and achieving up to 60% moderate repigmentation of the face and neck 3 months into therapy.54 The main adverse effects described were GI discomfort (12.5%), increased appetite (6.3%), and flushing (3.1%).55
Promoting repigmentationOf note (and patients should be informed), that the repigmentation process is slow, as it requires migration of melanocytes from healthy perilesional skin and/or differentiation of melanoblasts into melanocytes, migration from follicular stem-cell reservoirs, and production of new melanin.56,57 Areas with a high density of hair follicles respond more quickly. Moreover, UV radiation stimulates keratinocytes to produce growth factors that induce melanoblast differentiation into melanocytes and their proliferation.
Combined NB-UVB and targeted phototherapy (308-nm excimer laser or excimer light) along with calcineurin inhibitors (0.1% tacrolimus) or topical corticosteroids is the most effective therapeutic approach, achieving the best results in facial areas.46 Repigmentation is a slow process requiring 6–24 months.58,59 A meta-analysis showed that combining NB-UVB with calcineurin inhibitors achieved 75% repigmentation in nearly half of patients (47.5%) after a median 3-month follow-up – approximately 30% higher than calcineurin inhibitors alone (18.1%) – with greater efficacy on the face and neck (55.2%) than on the trunk and limbs (16.1%).60
Preventing relapseMore than 40% of lesions show new depigmentation 1 year after treatment withdrawal. Tacrolimus 0.1% applied twice weekly for 24 weeks has been shown to drop relapse risk from 40% (placebo group) down to 9.7%.61 Furthermore, although potent topical corticosteroids seem effective, they have not been evaluated in randomized prospective trials. For generalized vitiligo, NB-UVB administered 2–4 times per month may be useful, yet no published evidence exists.
Use of JAK inhibitors for the treatment of vitiligoJAK inhibitors may play an important role in treating vitiligo during the initiation, repigmentation, and persistence phases. Recently, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have approved topical ruxolitinib for the treatment of vitiligo in adults and adolescents older than 12 years.
Ruxolitinib is a non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory, selective, and potent inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2 kinases (Fig. 1).19,20,62–64 It is administered as a cream and has physicochemical properties suitable for transdermal application.63,65 This drug disrupts IFN-γ signaling by inhibiting JAK1 and JAK2.19,62–64 Its approval resulted from phase III clinical trials – the Topical Ruxolitinib Evaluation in Vitiligo Studies 1 and 2 (TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2) – which compared 1.5% ruxolitinib twice daily with placebo in 674 patients older than 12 years with non-segmental vitiligo.21 The trial included an initial 24-week double-blind phase and a subsequent 28-week open-label extension in which all patients received ruxolitinib twice daily. At week 24, ruxolitinib achieved 75% facial repigmentation (F-VASI75, Facial Vitiligo Area Scoring Index) in 29.8% (TRuE-V1) and 30.9% (TRuE-V2) of patients vs 7.4% and 11.4% in the placebo group, respectively.21
In a long-term 52-week analysis, ruxolitinib achieved F-VASI75 in 50.3% of patients. A total of 30.3% achieved 90% repigmentation (F-VASI90) and 74.6% achieved 50% repigmentation (F-VASI50).22 For the body (neck and trunk), 51.1% of patients achieved T-VASI50 (Total Body Vitiligo Area Scoring Index) at week 52.22 Regarding safety at 52 weeks, application-site reactions were the most common treatment-emergent adverse events, all mild or moderate, and none required treatment discontinuation. The most frequently reported adverse event was acne (5.8%). No treatment-related serious adverse events were observed.22,66
A long-term extension study to week 104 was conducted after week 52. Patients who achieved >90% facial repigmentation (F-VASI90) at week 52 were randomized to receive ruxolitinib 1.5% twice daily or placebo (Cohort A, n=116),25 whereas those who did not achieve F-VASI90 continued ruxolitinib 1.5% twice daily (Cohort B, n=342).23
At week 104, most patients (69.1%) in Cohort A who continued ruxolitinib did not relapse (relapse defined as loss of response to25
Most patients who relapsed were able to regain clinically meaningful (F-VASI75) or complete/almost complete (F-VASI90) facial repigmentation after restarting ruxolitinib. Among patients who relapsed after stopping treatment and restarted ruxolitinib (n=16), 75% regained F-VASI75 by week 12, and ∼70% regained F-VASI90 by week 15.25
Continuous application of ruxolitinib was associated with a lower risk of losing F-VASI90 response vs placebo (HR, 0.32; 95%CI, 0.19–0.61). After treatment discontinuation, the median time maintaining F-VASI90 was ∼6.5 months.25 The safety profile of ruxolitinib cream at 104 weeks remained consistent with earlier findings.
In addition to ruxolitinib, other JAK inhibitors under investigation for vitiligo include tofacitinib, baricitinib, ifidancitinib, ritlecitinib, povorcitinib, brepocitinib, and cerdulatinib.67–73Table 3 illustrates these agents, their mechanisms, and the principal results available to date.
JAK pathway inhibitors under investigation for the treatment of vitiligo.
| Drug | Inhibition mechanism | Main results |
|---|---|---|
| Ruxolitinib (topical) | JAK1/2 | Ruxolitinib 1.5% cream BID, 24 weeks• F-VASI75: 29.8–30.9%21• Phototherapy improves outcomes: F-VASI75 and T-VASI: 42% without phototherapy, 68% with phototherapy24 |
| Tofacitinib (oral) | JAK1/3 | Tofacitinib 5–10mg QD/BID• 5.4% BSA improvement in 5/10 patients with sun-exposed areas or areas treated only with phototherapy after 3 months68• VASI score reduction from 4.68 to 3.95 after 5 months69 |
| Baricitinib (oral) | JAK1/2 | Baricitinib 4mg/day, 4 weeks• VASI score improvement of 61.25% on trunk and 59.26–74.17% on face/neck70 |
| Ifidancitinib (oral) | JAK1/3 | • Ifidancitinib, 24 weeks• NCT03468855: results not yet available |
| Ritlecitinib (oral) | JAK3 | Ritlecitinib QD, 24 weeks• 100mg 4 weeks+50mg 20 weeks: F-VASI75 12.1%71• 200mg 4 weeks+50mg 20 weeks: F-VASI75 8.5%71• 50mg 24 weeks: F-VASI75 7.7%71• 30mg 24 weeks: F-VASI75 2.7%71• 10mg 24 weeks: F-VASI75 2.3%71 |
| Povorcitinib (oral) | JAK1 | Povorcitinib, 24 weeks• 15mg: T-VASI50 10.5%, F-VASI50 18.4%, F-VASI75 13.2%72• 45mg: T-VASI50 15.2%, F-VASI50 45.5%, F-VASI75 18.2%72• 75mg: T-VASI50 5.6%, F-VASI50 27.8%, F-VASI75 13.9%72• Povorcitinib, 52 weeks (15/45/75mg)• T-VASI50 34.0%, F-VASI75 45.6%73 |
| Brepocitinib (oral) | TYK2/JAK1 | Brepocitinib, 24 weeks• NCT03715829: results not yet available |
| Cerdulatinib (oral) | SYK/JAK | Cerdulatinib 0.37% gel• Results not yet available |
BID: twice daily; BSA: body surface area; F-VASI50: 50% facial repigmentation; F-VASI75: 75% facial repigmentation; QD: once daily; T-VASI50: 50% total body repigmentation.
Vitiligo is a disease with a high emotional burden.74 The visibility of lesions – particularly when affecting the face and hands, or more sensitive areas such as the genital region – can affect personal self-image and self-esteem and lead to social stigmatization. Its unpredictable and variable course may generate feelings of uncertainty and loss of control. Furthermore, the condition is often trivialized as a merely “cosmetic” issue involving skin spots, overlooking that it is an autoimmune disease often associated with psychological comorbidities (anxiety, depression) and psychosocial issues (stigma, sexual dysfunction, adjustment disorders, suicidal ideation, among others) that patients must face.74–80
Mental healthThe most frequent mental health comorbidities in vitiligo patients are anxiety and depression, with significantly higher prevalence than in healthy individuals. Several meta-analyses and systematic reviews have shown that vitiligo patients are 5 times more likely to experience depression.74,76 Up to 25% have experienced suicidal ideation. Other frequent features include feelings of stigmatization, low self-esteem, adjustment disorders, relationship difficulties (including sexual dysfunction), sleep disturbances, alexithymia, cognitive and behavioral alterations, and alcohol or substance abuse.74 Moreover, psychological comorbidities are more prevalent in vitiligo patients than in those with acne, alopecia areata, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, or urticaria.74,81
Of note, the Global VALIANT Study – an observational, cross-sectional study conducted in 17 countries including 3541 vitiligo patients older than 18 years (mean age, 38) – aimed to evaluate the emotional and psychosocial burden of vitiligo.82 Participants completed online interviews addressing disease features and treatments received, along with the PHQ-9 (Patient Health Questionnaire-9) to assess depression severity and the VIPs (Vitiligo Impact Patient Scale) to assess quality of life. Nearly one-third of participants reported that their mental and psychosocial health was affected by vitiligo.82 A total of 58.7% reported mental health disorders (anxiety, 28.8%; depression, 24.5%), and half of these were severe. Patients at highest risk for depressive symptoms were younger individuals, those with darker skin phototypes, those with >5% body surface area involvement, facial/hand involvement, and disease duration ≤2 years. Moderate-to-severe depressive symptoms were significantly more common among patients with facial lesions (60.2% vs 32.0% without facial lesions). Of all participants, 39.5% of Spanish patients (n=200) reported depression per PHQ-9 scoring.82
Quality of lifeIn addition to psychological and psychosocial comorbidities, vitiligo has moderate-to-severe effects on quality of life, affecting personal (self-image, self-esteem), sexual, family, social, and occupational domains.74,80,83,84 According to the Global VALIANT Study, >40% of patients described moderate-to-severe impairment in daily life.82 Other studies show that children and adolescents perceive daily stigmatization (93.2%) and bullying (21.7%) due to their vitiligo and often attempt to conceal their condition.85
When comparing quality of life in vitiligo with other diseases using the SF-36 questionnaire, vitiligo scores are comparable to psoriasis, dermatitis, arthritis, and even cancer and congestive heart failure.86
Although national mental-health strategies discuss stigma related to mental illness, there are no specific plans addressing the stigma caused by medical conditions such as vitiligo. That is, underlying diseases that affect self-perception are rarely acknowledged, and references to self-esteem largely relate to societal stigma toward individuals with mental disorders.
A study conducted in Spain under real-world clinical practice conditions showed that dermatologic treatment for vitiligo has decreased (from 33% of patients in 2015 to 25.8% in 2021), while mental-health treatment has increased (from 8.2% in 2015 to 11.9% in 2021).87
Of note, while quality of life is measured at a specific point in time, emotional impact results from the accumulation of prior experiences – namely, how vitiligo has affected the patient throughout their life.87 Treating the disease early after diagnosis improves patient experience and reduces emotional impact. Hence the importance of establishing effective treatments tailored to each individual to control disease activity and reduce psychological burden. Similarly, understanding, empathy, and respect from the patient's environment, as well as psychological support, are essential for learning to cope with vitiligo. Although psychotherapy does not improve the clinical course of vitiligo, it can help patients cope differently, avoid passive attitudes, become more engaged in treatment, and adopt a more holistic perspective of their condition.
ConclusionsDue to the improved understanding of the immunopathogenesis of vitiligo, this historically neglected or underestimated disease now has a more optimistic outlook. New therapeutic alternatives, such as topical ruxolitinib – a JAK-STAT pathway inhibitor – have demonstrated significant short- and mid-term repigmentation rates, helping reduce emotional burden and improve quality of life for patients.
FundingThis work was funded by Incyte.
Conflicts of interestJLLE has served as a consultant, participated in clinical trials, and/or received lecture fees from Almirall, Janssen, Leo Pharma, Lilly, AbbVie, Bioderma, Galderma, UCB, Novartis, Pierre-Fabre, Invasix, Isdin, and Incyte.
GSM has participated in research studies for Pfizer, AbbVie, and Incyte and/or received honoraria for lectures from Incyte and Leo Pharma.
SRA has served as a consultant, participated in clinical trials, and/or received lecture fees from AbbVie, Almirall, Amgen, Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, Leo Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, MSD-Schering-Plough, Incyte, Pfizer, and UCB.
The authors thank Content Ed Net, Madrid (Spain) and Fernando Sánchez Barbero for assistance in writing and editing. This support was funded by Incyte.