In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) enables monitoring of non-melanocytic skin cancers (NMSC) treated with non-invasive or minimally invasive therapies. This systematic review analyzed studies on NMSC treated with these therapies and monitored by RCM. A total of 56 articles were included, with 40 focusing on squamous conditions, such as actinic keratosis and squamous cell carcinoma, 15 on basal cell carcinoma (BCC), and 1 on extramammary Paget's disease. Evaluated therapies included ablative laser, cryosurgery, photodynamic therapy, 5-fluorouracil, imiquimod, and tirbanibulin, among others. RCM demonstrated complete response in squamous conditions with normalization of the honeycomb pattern and reduction of scaling and parakeratosis, frequently allowing for detection of subclinical malignancy. In BCC, RCM showed complete response as disappearance of tumor islands. RCM allows treatment optimization and early monitoring, even when inflammation hinders clinical assessment. It is recommended that RCM evaluations be performed starting at least 1 month after treatment for squamous conditions and 3 months for BCC.
Non-invasive or minimally invasive therapies such as ablative laser, cryosurgery, photodynamic therapy (PDT), imiquimod (IMQ), 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), ingenol mebutate (IM), or tirbanibulin, among others, constitute an alternative to surgery or radiotherapy for the treatment of non-melanocytic skin cancers (NMSC) or premalignant conditions.1–6 However, identifying incomplete tumor clearance or recurrence can be very challenging, since there is a notable local inflammation generated by these agents.1,7–9 Besides, clinically non-visible clusters of malignant cells may escape to non-invasive or minimally invasive therapies, impeding an optimal treatment response.1,7–9 In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) apart from helping in the diagnosis of skin lesions can be a complementary tool to evaluate the efficacy of non-invasive treatments accurately and without the need to obtain a biopsy in many cases.1–3,5–17 This systematic review will provide an overview of in vivo RCM as a tool for monitoring treatment response of NMSC.
Material and methodsWe conducted a systematic literature search across MEDLINE and Scopus databases on June 18th 2024. The search was limited to articles in English or Spanish, but no date restriction was applied. This study was registered with PROSPERO (CRD4(2023)477432) and followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement.18 Search query available in Supplementary material 5.
Eligibility criteriaInclusion and exclusion criteriaIncluded articles included those containing original data about patients with skin malignant or premalignant conditions (including basal cell carcinoma – BCC, squamous cell carcinoma – SCC, actinic keratosis – AK, actinic cheilitis, among others) that were treated with non-invasive or minimally invasive therapies, and whose response was assessed using RCM. Apart from randomized clinical trials (RCT) and large observational studies, case series and case reports were also included.
Patients with non-malignant conditions or those undergoing surgery or on systemic therapy as the main treatment modality were excluded. Similarly, studies that did not use RCM for assessing the response to treatment, those that did not include humans (e.g., basic and preclinical research), or studies that did not report treatment information were excluded. Meta-analysis, systematic and narrative reviews, guidelines, protocols, and conference abstracts were excluded, as well as articles written in a language other than Spanish or English.
Type of interventionA study was considered eligible if RCM was used to monitor noninvasive or minimally invasive treatment interventions, including lesion-directed procedures (e.g., cryosurgery, ablative laser therapy) or field-directed topical therapies (e.g., photodynamic therapy, diclofenac, 5-fluorouracil, imiquimod, tirbanibulin, piroxicam, and ingenol mebutate).
Patients who underwent surgical treatment after a non-invasive/minimally invasive therapy were also included, provided outcome data regarding the non-invasive/minimally invasive therapy was available (only this information was used). Complete response was assumed if no residual lesion remained, otherwise, outcome was categorized as treatment failure (including persistence, progression, or recurrence).
In those studies that included invasive therapies apart from non-invasive or minimally invasive therapies, only patients undergoing non-invasive treatments were selected.
Study selectionWe conducted initial title and abstract screening. Publications selected for eligibility assessment were evaluated by full-text reading by two authors (J.V.G. and S.G.). Disagreements were resolved by a third member (M.A.).
Quality assessmentRisk of bias (ROB) was assessed according to the recommendation by the Cochrane Collaboration, and was independently evaluated by two reviewers.19 Case reports were assumed to present multiple bias.20 The following items were assessed: selection biases, performance biases, detection biases, attrition biases, reporting biases, and other sources of bias (e.g., potential conflicts of interests, modifications of conditions influencing measurements). These items were classified as “low risk” (when no bias was identified), “high risk” (when bias was detected), or “unclear risk” (when there was not enough information). Quality rating of studies was done as follows: 1: RCT and systematic review with meta-analysis; 2: non-randomized controlled trials or prospective comparative cohort trials; 3: case–control studies and retrospective cohort studies; 4: case series and cross-sectional studies; and 5: case reports and opinion of experts.
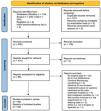
ResultsThe search yielded a total of 377 records. After duplicate removal, title and abstract screening, and not-retrievable article removal, 98 articles were full-text assessed for eligibility. Of these, 42 were excluded, finally including 56 articles in the review (see Fig. 1).
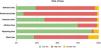
The percentage of studies with each risk grade are represented in Fig. 2, based on the researchers’ evaluation (see Supplementary data 6 for detailed information).
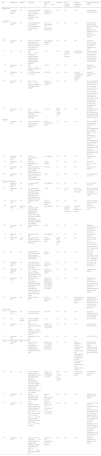
Squamous cell carcinoma and other squamous premalignant conditionsForty-one articles studying SCC and other squamous premalignant conditions were included (34 RCTs, large observational studies or case series, and 7 case reports), including AKs (31/41), actinic cheilitis (2/41), SCC (including Bowen's disease) (7/41), and Bowenoid papulosis (1/41) (Table 1 and Supplementary Tables 1 and 3). Regarding treatment modalities, there was only 1 study21 assessing the effectiveness of ablative laser for the treatment of AKs in 30 patients, showing a reduction of RCM features suggesting subclinical AKs. Two articles15,22 studied the efficacy profile of cryosurgery for treating AKs, reporting an improvement of the main features by RCM. Seven articles2,3,8,14,23–25 studied the efficacy profile of daily 5-FU 0.5% for 2–12 weeks in AKs, showing a complete response rate between 33.3% and 100%. The efficacy profile of IMQ 3.75–5% was assessed in 6 studies,4,13,17,26–28 achieving a complete response in a single case of SCC, and in a 23.1–90% for AKs. Ingenol mebutate 0.015–0.05% was evaluated in two studies, showing a complete response in three cases of actinic cheilitis,29 and an improvement of histological and RCM features right after ending the therapy in 10 cases of Aks.30 Several studies evaluated the efficacy profile of PDT, 3 of them for the treatment of in situ SCCs (13 lesions, including one Bowen's disease case),16,31,32 1 for treating invasive SCC (comprising 4 cases),33 and 13 for treating AKs with conventional or daylight PDT.6,13,15,30,34–42 These works showed a complete response rate of 63.6–100% for in situ SCC, 75% for invasive SCC, and 51.6–100% for AKs. Other therapies such as piroxicam, diclofenac, tirbanibulin, or 2,4,6-octatrienoic acid were used for the treatment of AKs in 5 studies,2,30,43–45 revealing an improvement of RCM features suggesting persistence of AKs. There were also seven reports39,46–50 of different combinations of the abovementioned therapies, showing a complete response rate of 67.7–82.9% for AKs, and 100% for case series of SCC and actinic cheilitis.
Monitoring the efficacy of non-invasive and minimally invasive treatment in squamous cell carcinoma and other premalignant keratinocytic lesions.
| Ref.a | RCM model | Disease | Treatment | Patient No. (F:M)±lesion No.b | Follow-up | Post-treatment histology | Outcome assessed by histology | Outcome assessed by RCMd,e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ablative laser | ||||||||
| 21(1*) | VivaScope 1500 and 3000 | AK | Self-controlled:Group 1: CO2-fractional laser (once every 3 weeks for 3 times)Group 2: No treatment | Group 1: 30 (0:30)Group 2: 30 (0:30) | 6 m | No | N/A | Improvement of features in Group 1 |
| Cryosurgery | ||||||||
| 22(1*) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | Self-controlled:Group 1: One cycle of cryosurgeryGroup 2: Two cryosurgery cycles | 23 (12:11) patientsGroup 1: 21 lesionsGroup 2: 23 lesions | 1 m | No | N/A | Improvement of features in both groups (significantly greater improvement of parakeratosis and epidermal inflammation in group 2) |
| 5-FU | ||||||||
| 14(4) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | 5-FU 5% in occlusion (twice daily for 2 weeks) followed by almond oil (2 weeks). This cycle was repeated twice | 7 (not defined) patients; 13 lesions | 0 mc | No | N/A | CR: 53.8% (7/13)TF: 13.4% (2/13)Drop-outs: 28.6% (2/7) patients; 30.8% (4/13) |
| 8(4) | N/A | AK | 5-FU 0.5%+10% salicylic acid (daily).Treatment duration:2-week treatment4-week treatment6-week treatment | 8 (1:7) | 0.5 m | Yes (only available for 4 patients) | CR confirmed in 4 patients | 2-week treatment: CR: 100% (1/1)4-week treatment: CR: 33.3% (1/3); TF: 66.7% (2/3)6-week treatment: CR: 100% (4/4) |
| 23(4) | VivaScope 3000 | AK | 5-FU 0.5%+10% salicylic acid (daily for 6 weeks) | 21 (0:21) | 0.5 m | No | N/A | Significant improvement of features |
| 24(4) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | 5-FU 5% (twice daily for 4 weeks) | 50 (38:12) | 1 m | Yes | CR: 54% (27/50)TF: 26% (13/40)Drop-outs: 20% (10/50) | Significant improvement of features |
| 25(1*) | VivaScope 3000 | AK | Group 1: 5-FU 0.5%+10% salicylic acid (daily for 12 weeks)Group 2: Placebo | Group 1: 17 (4:13)Group 2: 10 (1:9) | 2 m | No | N/A | Group 1:Reduction of subclinical AKs: 90% (95% CI, 72.1–107.1)Complete clearance: 64.7% (11/17)TF: 23.5% (4/17)Drop-outs: 11.8% (2/17)Group 2:Reduction of subclinical AKs: 47% (95% CI, 24.8–69.5)Complete clearance: 40% (4/10)TF: 40% (4/10)Drop-outs: 20% (2/10) |
| 3(4) | VivaScope 3000 | AK | 5-FU 0.5%+10% salicylic acid (daily for 4–12 weeks, depending on the response) | 14 (2:12) | Median 30 w (range: 5–39.1 w) | No | N/A | Overall:CR: 42.9% (6/14)TF: 57.1% (8/14)Patients who underwent 12-week treatment:CR: 60% (3/5)TF: 40% (2/5) |
| Imiquimod | ||||||||
| 26(1*) | VivaScope 1000 | AK | Group 1: IMQ 5% (3 times/week for 4 weeks)Group 2: Placebo | Group 1: 13 (0:13)Group 2: 4 (0:4) | 1 m | N/A | N/A | Group 1:At week 4 of treatment:CR: 7.7% (1/13)TF: 69.2% (9/13)Indeterminate: 23.1% (3/13)At week 4 after the end of treatment:CR: 23.1% (3/13)TF: 53.8% (7/13)Indeterminate: 23.1% (3/13)Group 2:At week 4 of treatmentTF: 100% (4/4)At week 4 after the end of treatment:TF: 75% (3/4)Indeterminate: 25% (1/4) |
| 13(4) | VivaScope 1000 and 1500 | AK | IMQ 5% (3 times/week for 4 weeks) | 4 (not defined) | 1.5 m | No | N/A | Improvement of features |
| 17(4) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | IMQ 5% (3 times/week for 4 weeks) | 11 (not defined) | 1 m | No | N/A | CR: 81.8% (9/11)TF: 18.2% (2/11) |
| 27(4) | VivaScope 3000 | AK | IMQ 3.75% (daily for 2 weeks; repeat cycle after a 2-week treatment-free period) | 31 (2:29) | 2 m | No | N/A | Improvement of features |
| 28(4) | VivaScope 3000 | AK | IMQ 3.75% (daily for 2 weeks; repeat cycle after a 2-week treatment-free period) | 10 (3:7) | 1 m | No | N/A | CR: 90% (9/10)TF: 10% (1/10) |
| Photodynamic therapy | ||||||||
| 13(4) | VivaScope 1000 and 1500 | AK | Conventional PDT with ALA | 4 (not defined) | 1.5 m | No | N/A | CR: 75% (3/4)TF: 25% (1/4) |
| 34(4) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | Conventional PDT with MAL; 2 sessions separated 1 week apart**Patients with persistence at 3 m were administered an additional PDT cycle | 10 (2:8) | 12 m | Yes (at 3m) | At 3 m:CR: 70% (7/10)TF: 30% (3/10) | After 3 months:CR: 70% (7/10)TF: 30% (3/10)After 12 months:CR: 100% (10/10) |
| 35(4) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | Daylight PDT with MAL | 20 (6:14) patients; 40 lesions | 3 m | No | N/A | CR: 57.5% (23/40 lesions)TF: 42.5% (17/40) |
| 33(2) | VivaScope 1500 | Invasive SCC | Group 1: Conventional PDT with 5-ALA after curettage of the hyperkeratotic surface. Two cycles, each cycle consisting of 5 sessions administered every 7 daysGroup 2: Surgery (not included) | 4 (not defined) | 24 m | Yes (only treatment failure confirmed) | Treatment failure confirmed in 1 patient | CR: 75% (3/4 lesions)TF: 25% (1/4) |
| 36(4) | VivaScope 3000 | AK | Daylight PDT with MAL | 10 (8:2) | 2 m | No | N/A | Significant improvement: 40% (4/10)TF: 50% (5/10)Drop-out: 10% (1/10) |
| 37(4) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | Daylight PDT with MAL | 6 (not defined) | 3 m | No | N/A | Improvement of features |
| 16(4) | VivaScope 1500 | In situ SCC | Conventional PDT with MAL 16%.Two sessions separated 1 week apart | 10 (8:2) patients; 11 lesions | Median 24 m (range. 3–30 m) | No | N/A | At 3 months:CR: 63.6% (7/11)TF: 36.4% (4/11)Overall:CR: 45.4% (5/11)TF: Persistence: 36.4% (4/11); Recurrence: 18.2% (2/11) |
| 6(4) | N/A | AK | Conventional PDT with 5-ALA 20%.One cycle included 4 treatments, with 7–10 days intervals | 32 (not defined) | 6 m | No | N/A | CR: 71.9% (23/32)TF: Persistence: 12.5% (4/32); Recurrence: 3.1% (1/32)Drop-outs: 12.5% (4/32) |
| 42(4) | VivaScope 1500 and 3000 | AK | Conventional PDT with 5-ALA 10%Three sessions separated 1 month apart | 16 (13:3) patients; 20 lesions | 1 m | No | N/A | CR: 85% (17/20 lesions)TF: 15% (3/20 lesions) |
| 38(4) | VivaScope 1500 and 3000 | AK | PDT with 5-ALA 10% for 3h under occlusion; posterior irradiation with pulsed red light, at 630nm | 52 (34:18) patients; 300 lesions | 3 m | No | N/A | Improvement of features |
| 40(1*) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | Daylight PDT with MAL. Two groups:Group 1 underwent curettage of the lesions prior to PDTGroup 2 underwent skin preparation with 30% urea cream (twice a day for 7 days) prior to PDT | Group 1: 20 patients (not defined); 337 lesionsGroup 2: 20 patients (not defined); 421 lesions | 3 m | No | N/A | Reduction in the number of AK lesions:Group 1: 58.7% (from 337 to 130)Group 2: 54.7% (from 421 to 169)Improvement of features in both groups |
| 41(4) | VivaScope 3000 | AK | Daylight PDT with MAL | 24 (13:11) patients; 227 lesions | 3 m | Yes | Improvement of featuresMissing data: 8.1% (3/24) | Improvement of featuresSignificant reduction in the total number of AK and the median number of lesions per patient |
| Other therapies | ||||||||
| 43(4) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | Piroxicam 0.8% twice a day for 6 months | 54 (12:42) | 0 mc | No | N/A | Significant reduction in AK No. and severity.Drop-out: 9.3% (9/54) |
| 29(4) | N/A | Actinic cheilitis | Ingenol mebutate 0.015% daily for 3 days | 3 (2:1) | 1 m | No | N/A | CR: 100% (3/3) |
| 44(1*) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | Group 1: 2,4,6-octatrienoic acid daily for 3 months+urea 15%Group 2: Placebo cream containing urea 15% | Group 1: 36 (16:20)Group 2: 34 (13:21) | 3 m | No | N/A | Improvement of features in group 1 |
| 45(4) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | tirbanibulin 1% for 5 days | 10 (1:9) | 1 m | No | N/A | CR: 100% (10/10) |
| Studies including groups with different therapies | ||||||||
| 2(1*) | VivaScope 3000 | AK | Group 1: 5% 5-FU (once daily; 5 times/week for 4 weeks)Group 2: Diclofenac sodium 3% (twice daily for 60 days) | Group 1: 15 (0:15)Group 2: 15 (0:15)At least 3 AKs in each patient | 2 m | Yes | Group 1: Reduction in the total number of AKs in 53.98%. Improvement of field cancerization in 57.13%Group 2: Reduction in the total number of AKs in 52.99%. Improvement of field cancerization in 62.45% | Improvement of features in both groups (inflammatory cell reduction in RCM was reduced more markedly in Group 1) |
| 30(3) | N/A | AK | Group 1: Ingenol mebutate 0.015% (face/scalp) or 0.05% (trunk/extremities) (daily for 3 days)Group 2: Conventional PDT with MAL; 2 sessions separated 4 weeks one from each otherGroup 3: Piroxicam (twice daily for 16 weeks) | Group 1: 10 (2:8)Group 2: 10 (2:8)Group 3: 10 (2:8) | Group 1: 4 mGroup 2: 3 mGroup 3: 0 mc | Yes | Improvement of features in all groups | Improvement of features in all groups |
| 15(1*) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | Group 1: Conventional PDT with MALGroup 2: One cryosurgery cycle | Group 1: 10 (not defined)Group 2: 10 (not defined) | 6 m | No | N/A | Improvement of features in both groups |
| 39(1*) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | Group 1: Conventional PDT with ALA 20%Group 2: Microneedling (12 needles, depth of 400μm)+PDT with ALA 20%Group 3: CO2 fractional laser+PDT with ALA 20%Group 4: Contact cryosurgery with a cotton bud+PDT with ALA 20% | Group 1: 31 (10:21)Group 2: 31 (11:20)Group 3: 30 (11:19)Group 4: 35 (13:22) | 3–12 m | No | N/A | Group 1: CR: 51.6% (17/31)TF: Persistence: 45.2% (14/31); Recurrence: 12.5% (2/16)Group 2: CR: 67.7% (21/31)TF: Persistence: 29% (9/31); Recurrence: 12.5% (1/20)Group 3: CR: 76.7% (23/30)TF: Persistence: 20% (6/30); Recurrence: 12.5% (1/19)Group 4: CR: 82.9% (29/35)TF: Persistence: 14.3% (5/35); Recurrence: 12.5% (1/24) |
| 46(2) | VivaScope 1500 | AK | Group 1: One cycle cryosurgery+IM 0.015% (daily for 3 days) 2 weeks laterGroup 2: Ingenol mebutate 0.015% (daily for 3 days)+1 cycle cryosurgery 2 weeks later | Group 1: 12 (not defined)Group 2: 14 (not defined) | 1.5 m | No | N/A | Significant improvement of features in both groups |
5-FU, 5-fluorouracil; AK, actinic keratosis; ALA, aminolevulinic acid; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval; F, female; m, months; G1, Grade 1 actinic keratosis; G2, Grade 2 actinic keratosis; LED, light-emitting diode; M, male; MAL, methyl aminolevulinate; N/A, not available; PDT, photodynamic therapy; RCM, reflectance confocal microscopy; Ref., reference; TF, treatment failure; w, weeks.
Overall, RCM showed restoration of a normal honeycomb pattern and reduction of scaling and parakeratosis (nucleated keratinocytes in the stratum corneum) in patients with complete response. Clinical and dermoscopic evaluation frequently overestimated complete response rate vs RCM, as the latter detected persistence of AKs despite having no clinical lesions. Within the first weeks after treatment, apart from the findings related to the malignant/premalignant condition, inflammation in form of exocytosis, vesicles, and dendritic cells in the epidermis could be detected in RCM, even when clinical and dermoscopic evaluation was not feasible due to local inflammatory reaction (even though intense inflammation could hamper RCM assessment). Inflammatory cells in dermis could also be observed.
When available, histology agreed in most of the cases with findings in RCM.
Basal cell carcinomaA total of 15 studies on non-invasive treatment of BCCs were included, including superficial, nodular, and mixed type BCCs (Table 2 and Supplementary Tables 2 and 4). Four articles51–54 studied the efficacy profile of ablative laser (CO2 and Er:YAG), yielding a complete response rate of 33.3–100%, being the response rates higher in superficial BCCs vs the rest of histological subtypes. Two studies47,55 assessed the efficacy profile of cryosurgery, showing a complete response rate of 20–100%. Four studies5,9,56,57 performed treatment with imiquimod 5%, showing a complete response rate of 53.8–100%. Three articles1,7,58 studied PDT with MAL and 5-ALA, presenting a complete response rate of 25–100%. Furthermore, there was 1 study59 in which combination of ablative laser and ingenol mebutate was tested, showing a complete response rate of 61.5–85.7%, and a case report in which ablative laser and conventional PDT were combined, showing a complete response.
Monitoring the efficacy of non-invasive and minimally invasive treatment in basal cell carcinoma.
| Ref.a | RCM model | Disease | Treatment | Patient No. (F:M)±lesion Nob | Follow-up | Post-treatment histology | Outcome assessed by histology | Outcome assessed by RCMd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ablative laser | ||||||||
| 54(4) | VivaScope 1500 | Superficial/early nodular BCCs | Er:YAG laser ablation (4–12 passes) | 2 (2:0) | 0 mc | Yes | CR: 100% (2/2) | CR: 100% (2/2) |
| 51(4) | VivaScope 1500 | Subgroup 1: Superficial BCCsSubgroup 2: Mixed type BCCs | CO2 laser ablation (up to 3 passes)**Posterior MMS | Subgroup 1: 4 (2:2) patients; 5 lesionsSubgroup 2: 3 (2:1) | 0 mc | Yes | Subgroup 1: CR: 100% (5/5)Subgroup 2: CR: 33.3% (1/3); TF: 66.7% (2/3) | Subgroup 1: CR: 100% (5/5)Subgroup 2: CR: 33.3% (1/3); TF: 66.7% (2/3) |
| 52(2) | VivaScope 1500 and 3000 | Subgroup 1: Superficial and early nodular (×4), infiltrative (×1) and intradermal (×1) BCCsSubgroup 2: Superficial BCCsSubgroup 3: Superficial (×26), superficial and early nodular (×6), and early nodular (×2) BCCs | Subgroup 1: Er:YAG laser ablation (7-9 passes)*Subgroup 2: Er:YAG laser ablation (5–7 passes)Subgroup 3: Er:YAG laser ablation (5–11 passes; in patients with residual BCCs after 1 ablation treatment an additional cycle of 2–4 passes was performed)*Posterior Mohs micrographic surgery(self-controlled: treated vs non treated areas within the same BCC) | Subgroup 1: 6 lesions (number of patients not defined)Subgroup 2: 4 lesions (number of patients not defined)Subgroup 3: 15 (not defined) patients34 lesions | Subgroup 1: 0 mcSubgroup 2: 0 mcSubgroup 3: Mean 13 m (range: 1–21 m) | Subgroup 1: YesSubgroup 2: YesSubgroup 3: No | Subgroup 1: CR: 33.3% (2/6)TF: 66.7% (4/6)Subgroup 2: CR: 100% (4/4)Subgroup 3: N/A | Subgroup 1: CR: 33.3% (2/6); TF: Persistence: 50% (3/6); Suspicion of persistence: 16.7% (1/6)Subgroup 2: CR: 100% (4/4Subgroup 3:After 1 ablation cycle:CR: 79.4% (27/34)TF: 20.6% (7/34)Overall (after additional ablation cycles):CR: 91.2% (31/34)TF: Persistence: 2.9% (1/34); Recurrence: 5.9% (2/34) |
| 53(4) | VivaScope 3000 | Superficial (×21) and mixed type (nodular, superficial and infiltrative) (×1) BCCs | CO2 laser ablationIn lesions (n=5) showing BCC persistence after 1 pass additional passes were performed (mean: 3.6 passes; range: 2–8) | 9 (4:5) patients22 lesions | Median 28.5 m (range: 22–32 m) | No | N/A | Immediately after 1 laser pass:CR: 77.3% (17/22)TF: 22.7% (5/22)At 12 months [considering patients who completed the follow up (6/9 patients; 17/22 lesions)]:CR: 100% (6/6 patients, 17/17 lesions) |
| Cryosurgery | ||||||||
| 47(4) | VivaScope 1000 | Superficial BCCs | 2 cryosurgery cycles | 5 patients (3:2); 10 lesions | 3 m | Yes | CR: 80% (8/10)TF: 20% (2/10) | CR: 20% (2/10)TF: 80% (8/10) |
| 55(4) | VivaScope 1500 | Superficial (×3) and nodular (×4) BCCs | 2 cryosurgery cycles | 7 (2:5) | 2 m | No | N/A | CR: 100% (7/7) |
| Imiquimod | ||||||||
| 56(1*) | VivaScope 1000 | Superficial (×2) and nodular (×10) BCCs | Group 1: IMQ 5% (5 times/week for 6 weeks)*Group 2: Placebo**MMS performed 2–4 weeks after treatment | Group 1: 12 (4:8)Group 2: 12 (not defined) | 0.5–1 m | Yes | Group 1: CR: 67% (8/12)TF: 33% (4/12)Group 2: N/A | Compared with histologyGroup 1: NPV: 85.7% (6/7); PPV: 60% (3/5)Placebo group: NPV: 33.3% (1/3); PPV: 100% (8/8) |
| 57(4) | VivaScope 1500 and 3000 | BCC (subtype not defined) | IMQ (% not defined) (5 days/week for 6 weeks) | 8 patients (4:4); 13 lesions | 6 m | No | N/A | CR: 53.8% (7/13)TF: 46.2% (6/13) |
| 9(4) | VivaScope 1500 | Multifocal superficial BCCs | IMQ 5% (5 times/week for 8–28 weeks; mean 18.6±6.9 weeks)In case of insufficient response, IMQ was continued and response was reevaluated every 2 weeks, until clearance | 4 patients (3:1)34 lesions | 44–24 w (52 w since start of IMQ) | No | N/A | At week 12: CR: 64.7% (22/34); TF: 35.3% (12/34)At week 24: CR: 76.5% (26/34); F 23.5% (8/34)At week 52: CR: 88.2% (30/34); TF: 11.8% (4/34) |
| Photodynamic therapy | ||||||||
| 58(4) | VivaScope 1500 | Superficial or nodular BCCs | Conventional PDT with MALLesions were treated with 1–3 cyclesLesions that persisted after PDT were surgically removed or treated with alternative therapies such as imiquimod. | 6 patients (3:3)274 lesions | 36 m | Yes (only treatment failure confirmed) | Not available | At month 3 of follow-up, clearance of 25–67% of the BCCs was seenAfter 36 months, in some of the patients, recurrence of some of the lesions occurred (percentage not defined) |
| 1(4) | VivaScope 1500 | Nodular BCCs (×2); subtype not defined for the rest of the lesions | Conventional PDT with 5-ALA 10%*Patients with residual BCC underwent a second cycle of PDT | 10 (not defined) patients; 12 lesions (two nodular subtype and remaining undefined) | 18 m | Yes (only treatment failure confirmed) | Treatment failure confirmed at the 1-month of follow-up in 2 patients | At 1 month:CR: 83.3% (10/12)TF: 16.7% (2/12)*At 18 months:CR: 100% (12/12) |
| 7(4) | VivaScope 1500 | Superficial (×18), nodular (×1) or micronodular (×1) BCCs | Conventional PDT with MAL 16%**Patients with residual BCC [superficial (×3), nodular (×1), and micronodular (×1)] underwent a second cycle of PDT | 20 (10:10) | 12 m | Yes | At 3 months:CR: 75% (15/20)TF: 15% (5/20) | At 3 months:CR: 75% (15/20)TF: 15% (5/20)At month 12:CR: 100% (20/20) |
| Combined therapies | ||||||||
| 59(4) | VivaScope 1500 | Subgroup 1: Superficial BCCsSubgroup 2: Nodular BCCs | CO2 laser ablation+immediate application of ingenol mebutate 0.015% for 3 days (scalp or face) or 0.05% for 2 days (other regions) under occlusion**A second cycle was applied for residual BCC or inconclusive RCM imaging after 1 m | Subgroup 1: 7 (3:4)Subgroup 2: 13 (6:7) | 3 m | Yes | Subgroup 1:CR: 85.7% (6/7)TF: 14.3% (1/7)Subgroup 2:CR: 61.5% (8/13)TF: 38.5% (5/13) | Subgroup 1:At 1 month:TF: 71.4% (5/7)Not applicable or inconclusive imagingd: 28.6% (2/7)At 3 months:CR: 71.4% (5/7)F. 14.3% (1/7)Inconclusive imagingd: 14.3% (1/7)Subgroup 2:At 1 month:CR: 7.7% (1/13)TF: 76.9% (10/13)Not applicable or inconclusive imaginge: 15.4% (2/13)At 3 months:CR: 53.8% (7/13)TF: 38.5% (5/13)Inconclusive imaginge: 7.7% (1/13) |
BCC, basal cell carcinoma; F, female; LC, Langerhans cells; M, male; MMS, Mohs micrographic surgery; N/A, not available; NPV, negative predictive value; PPV, positive predictive value; RCM, reflectance confocal microscopy; Ref., reference; TF, treatment failure.
In patients with complete response, RCM evidenced disappearance of tumor islands with streaming of basal cells and palisading. Conversely, residual tumor was mainly detected as tumor islands composed of cells with elongated nuclei, accompanied by large blood vessels on some occasions. Overall RCM and histology yielded similar results regarding complete response and treatment failure rates, when both performed; nonetheless, in some studies RCM underestimated the efficacy profile of the therapy, showing findings suggestive of treatment failure, while histology showed a complete clearance.59
Other lesionsOne of the included articles60 studied the utility of RCM for monitorization of extramammary Paget's disease treated with imiquimod 5%, 5 times/week for 12 weeks (n=5), and 1 case treated with conventional PDT. A complete response rate of 80% (4/5) in the IMQ group, and 100% (1/1) in the PDT group was observed. One of the patients treated with IMQ presented a recurrence of the disease (time to recurrence not specified).
DiscussionEven though there was a great heterogeneity among publications, especially regarding follow-up periods, overall, RCM helped assess treatment response accurately, determining the need to continue or to stop treatment despite the clinical or dermoscopic appearance, showing agreement in most of the cases with histology, when available.
Squamous cell carcinoma and other squamous premalignant conditionsDespite the scarce literature studying it, CO2 ablative laser proved effective treating clinical evident AK, and even subclinical Aks.21
Regarding cryosurgery, Mota et al.22 compared the effectiveness of 1 vs 2 cycles of cryosurgery, and even though clinical results were similar, RCM proved more effective with 2 cryosurgery cycles. On the other hand, Curiel-Lewandrowski et al.15 concluded that Grade 1 AKs showed a more evident and durable response compared to Grade 2 AKs, and that even though some features may show a reduction at 3 months post-treatment, they could reappear at 6 months. This fact highlights the importance of performing follow-up with tools capable of detecting early recurrences of lesions. Moreover, they also suggested that the most reliable features for monitoring AK response are stratum corneum disruptions, hyperkeratosis, atypical honeycomb pattern including epidermal disarrangement.15
Regarding 5-FU, the available studies detected a reduction in the distinctive RCM findings indicative of AK at the end of the follow-up.2,3,8,14,23–25 Nonetheless, RCM allowed the detection of persistence of subclinical AKs after treatment.3 A RCT compared 5-FU against sodium diclofenac yielding no differences regarding the reduction in the number of AKs or improving field cancerization.2 Ulrich et al.25 compared 5-FU against placebo and despite not finding statistically significant differences in terms of complete response rate for AKs, they did find statistical significance in reducing the number of subclinical AKs. Regarding imiquimod, RCM allowed to detect persistence of AKs even when clinically was free of disease, and thus to guide continuation of the treatment until complete response was achieved.17,26 Furthermore, Benati et al.27 stated that RCM allowed assessment of treated field right 2 weeks after initiation of imiquimod, even though clinical evaluation was not possible due to the inflammatory response. On the other hand, Campione et al.30 studied the utility of ingenol mebutate for AKs, showing that reduction of hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis were the first signs of response, followed by the normalization of the honeycomb pattern.
Regarding PDT, in several studies,34–36,39 clinical and dermoscopic assessment overestimated AK clearance, and thus RCM allowed to administer further PDT cycles when needed. Moreover, Xiang et al.33 suggested that the restoration of a typical honeycomb pattern was the most reliable marker of response to treatment in invasive SCC. Similarly, Curiel-Lewandrowski et al.15 suggested that the improvement of the atypical honeycomb pattern, hyperkeratosis, epidermal disarrangement, and stratum corneum disruptions were reliable markers of treatment response. Moreover, they manifested that response to treatment would be more evident and long-lasting in Grade 1 AKs and that even though some features were resolved at 3 months, they could reappear by 6 months. Similarly, Campione et al.30 stated that reduction of hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis were the first sign of response, followed by the normalization of the honeycomb pattern. On the other hand, Bandeira de Melo Cavalcante et al.41 found a poor agreement between RCM and histology after treating AKs with PDT (56.3% for atypical cells; 25% for dysplasia; no agreement for elastosis). The authors hypothesized that this could happen due to two different people evaluating the results of the techniques.
Besides, Pasquali et al.46 studied the efficacy profile of the combination of cryosurgery and ingenol mebutate in AKs, showing no difference according to the order of administration of both treatments. Nonetheless, a milder inflammatory skin reaction was seen when ingenol mebutate was administered first, suggesting this regimen as the preferred option due to a better tolerability.
Basal cell carcinomaRegarding treatment of BCC with ablative laser, it should be stated that most of the studies lacked a follow-up, as they only assessed effectiveness of the therapy immediately after performing laser. Sierra et al.52 suggested that the two recurrences observed in their study may have resulted from residual BCCs involving deep structures that were not detectable by RCM, leading to suboptimal outcomes with RCM-guided laser ablation.
Regarding RCM-monitorization of BCCs treated with cryosurgery, in the study of Ahlgrimm-Siess et al.,47 RCM underestimated the effectiveness of cryosurgery vs histology, suggesting that the scarring process may interfere with RCM image interpretation. Moreover, these authors highlighted that histologic clearance only occurred in those 8/10 lesions showing an early dermal reaction at RCM (bright round-polygonal dermal structures at 5h vs the additional 2/10 developing these changes at 24h), suggesting a possible response predictor starting at early evaluations. On the other hand, Pasquali et al.55 suggested that the slowly-progressive disappearance of BCC features may reflect the time needed by the immune system to activate and remove tumor cells. They also raised awareness of the possibility of pseudocysts being mistaken for tumor nest persistence.
Regarding IMQ, a case series by Zou et al.9 reported the presence of dendritic structures and bright epidermal particles at week 12. Similarly, Sahu et al.57 reported that an increased inflammation with scarce vasculature in RCM could predict a better response to IMQ. These structures may be predictors of response.
Regarding PDT, of note, two studies on RCM showed subclinical persistence of BCCs, allowing further treatment and thus avoiding recurrences.1,7 Similarly, Longo et al.1 raised awareness of the different appearance of residual BCCs after treatment with PDT compared to non-treated BCCs, as blurred or faint tumor islands could represent the only findings tumor persistence vs the dark silhouettes seen in non-treated BCC. These authors also reported that the activated LC and inflammatory cells would already appear one week after PDT lasting 1 month, representing a transient activation of the immune system.1
Finally, Banzhaf et al.59 studied the efficacy profile of combining ablative laser with ingenol mebutate, reaching higher complete response rates for superficial BCCs vs nodular BCCs. In this work, RCM was able to detect subclinical BCC persistence. Even though it did not reach statistical significance, the authors found a tendency of a better response to 0.05% of IM vs 0.015%.
Suggested RCM follow-up tips:In squamous tumors, RCM evaluation within the first 4 weeks after treatment showed an inflammatory response with the presence of dendritic cells supporting the hypothesis that the immune system may take several weeks to eliminate tumor cells.2,4,13,23,27,31 Similarly, in BCCs, an RCM evaluation within the first 6 weeks after treatment also showed inflammation, including abundant Langerhans cells, and persistence of tumor nests with acute changes such as necrotic basal cells or nest detachment.1,5,47,51,53,55,58,61 Tumor persistence may still be observed by 3 months,9,34,47,58,59,61 while at a later point in the follow up (e.g., 12–18 months) no signs of tumor can be seen in patients with complete response.1,7,9,61 Thus, even though more evidence is needed, it is suggested that RCM complete response assessment is conducted starting at least 4 weeks into therapy in squamous conditions, especially AKs, and starting at least 3 months into therapy in BCCs.
Regarding predictor markers of response, in case of AKs, it has been stated that the first sign is the reduction of hyper and parakeratosis, followed by the normalization of the honeycomb pattern.15,30,33 In BCC treatment, an early evaluation after cryosurgery, may help predict response, as the presence of a dermal reaction within the first 5h may predict a better response, compared with apparition of this reaction by 12h.47 Features suggesting a better response to IMQ can also be seen at later points during follow up, such as increased inflammation and bright epidermal particles.9,57 During follow-up, recurrence of treated BCCs may appear as blurred islands, compared to the dark silhouettes seen in non-treated BCCs.1 In addition, it should be highlighted the importance of long follow-up periods as there might be late recurrences.52,58
LimitationsFirst, most of the identified studies presented risk of bias in more than one of the assessed items. Second, follow-up periods and treatment regimens were heterogeneous between studies. Nonetheless, combining the available results some suggestions could be made regarding follow-up time of non-invasively treated lesions with RMC. Thus, even though some suggestions were presented herein, larger studies with homogeneous protocols are needed to reach more robust recommendations.
ConclusionsReflectance confocal microscopy allows the optimization of non-invasive or minimally invasive treatment of non-melanocytic skin cancer, by helping to monitor their response and adjust the need for discontinuation of the therapies or additional treatments. Particularly, RCM detected persistent lesions even when clinical and dermoscopic examinations were normal, allowing to continue the treatment until a complete response was achieved, and thus avoiding evitable recurrences. Similarly, it may be of great help for detecting early recurrences without the need of a biopsy. Furthermore, RCM could be of use for early monitorization of non-invasive or minimally invasive treatments, as the progression of the features of the lesions can be monitored even when the inflammatory response hinders clinical and dermoscopic evaluation.
Even though more evidence is needed, it is suggested that response assessment with RCM is conducted starting at least 4 weeks into therapy in the case of squamous conditions, particularly actinic keratosis, and starting at least 3 months into therapy in the case of basal cell carcinomas, considering that earlier evaluations could still show persistence of tumoral cells and inflammation. Nonetheless, longer follow-up periods are of the utmost importance in order to detect recurrences.
Conflicts of interestJMVG declared to have received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Almirall, Novartis, UCB, Sanofi/Genzyme, Pierre Fabre, Lilly, ISDIN, LEO Pharma, and Janssen. MRGH reported receiving support for attending meetings and/or travel from Almirall, Novartis, UCB, Sanofi/Genzyme, Lilly, Pierre Fabre, LEO Pharma, Janssen, AbbVie, and Viatris, and honoraria for lectures from Sanofi/Genzyme and AbbVie. MA reported receiving support for attending meetings from Helsinn and Recordati Rare Diseases; consulting fees from Pierre Fabre; honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from Almirall, Avène, and Kyowa Kirin; and participation on data safety monitoring boards or advisory boards for Kyowa Kirin and Almirall. SG declared no conflicts of interest.
Uncited reference62.