The recent report by Hiraldo-Gamero et al.1 on the use of 5% imiquimod cream to treat extramammary Paget disease (EMPD) confirms the growing interest in this new nonsurgical treatment option for this disease. In 2009 we reported the results obtained in the treatment of 3 cases of EMPD of the vulva with clinical and pathologic features similar to those described by Hiraldo-Gamero.2
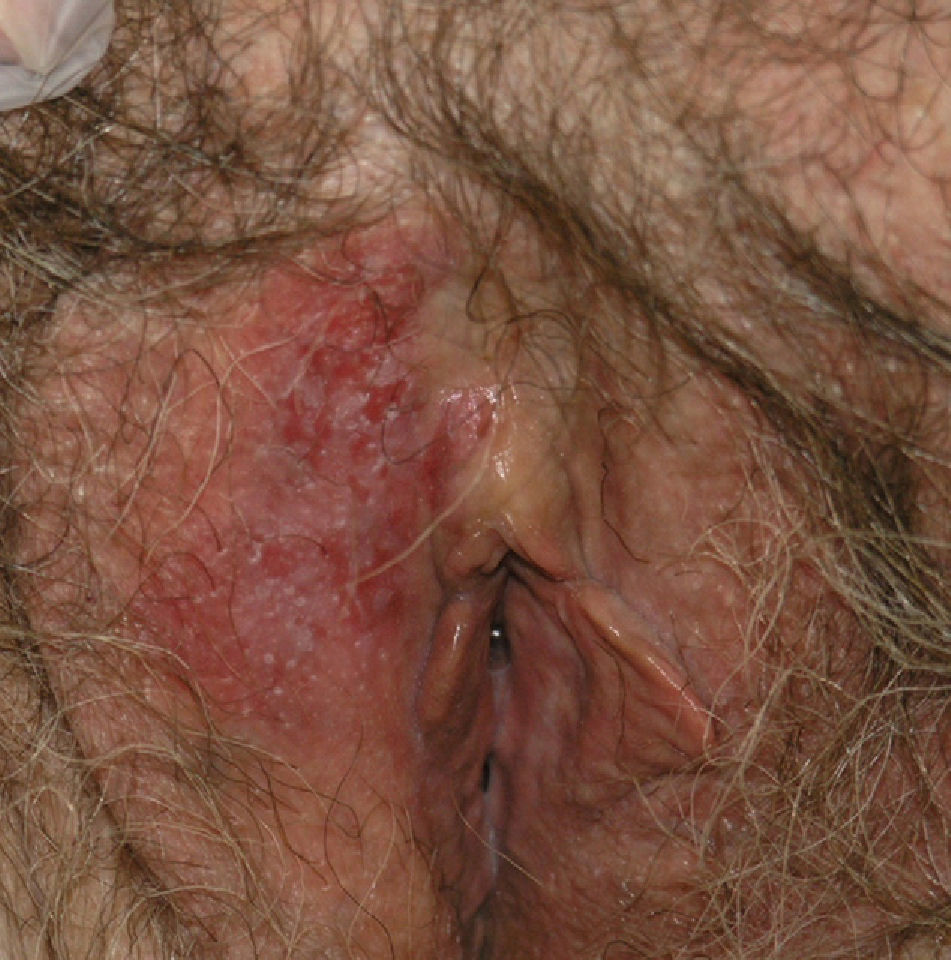
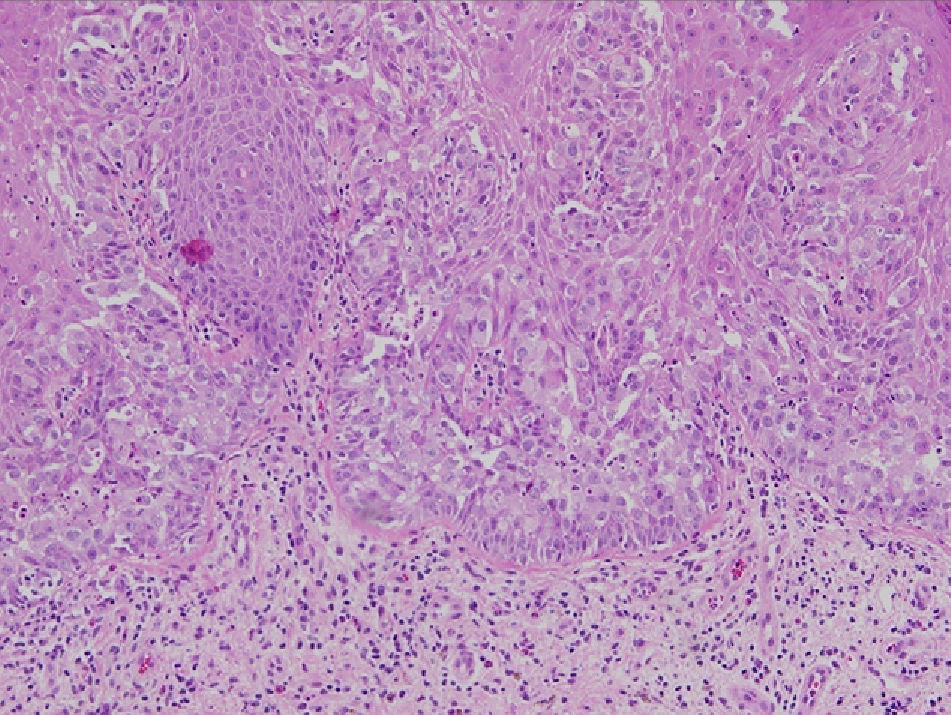
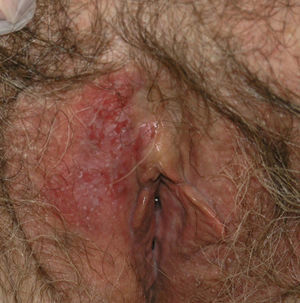
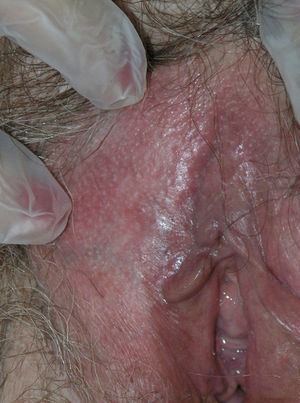
The 3 patients, aged 66, 58, and 82 years, had vulvar lesions up to 5cm in diameter (Fig. 1). In all 3 cases, the results of multiple biopsies (Fig. 2) revealed exclusively intraepidermal involvement, and exhaustive screening ruled out the possibility of underlying malignancy. Bearing in mind the comorbid conditions present in each case, treatment with imiquimod was chosen to avoid the risks associated with surgical excision, the approach traditionally used to treat such tumors. The regimen used was once daily application of 5% imiquimod cream for 3 weeks followed by application on alternate days for a further 13 weeks. All 3 patients completed treatment despite episodes of inflammation and moderate pain. Control biopsies were performed at 6 and 12 months. The 3 patients were followed up clinically every 3 months for 1 year after treatment and every 6 months thereafter. At the time of writing, they have completed a follow-up period of 53 months and remain in complete remission (Fig. 3). Green et al.,3 who recently reviewed reports in the literature on the use of imiquimod in EMPD, found complete remission of the disease in 21 of the 27 reported cases (78%). The factors that influence the success or failure of imiquimod therapy in this setting have not yet been clearly established. Factors that might explain the variability of response to treatment include the size of the lesion, its variable thickness in different areas, and the presence of extensive adnexal involvement.
We agree with Hiraldo-Gamero that the small number of published cases makes it difficult to draw conclusions concerning the efficacy and safety of 5% imiquimod cream in selected cases of EMPD. Our report provides additional evidence on the medium-term safety of this treatment and represents the longest follow-up period free of disease reported in the dermatologic literature.
Please cite this article as: Herranz P, Sendagorta E, Feito M, Gómez-Fernandez C. Remisión mantenida de la enfermedad de Paget extramamaria tras tratamiento con imiquimod al 5% en crema. Actas Dermosifiliogr.2012;103:742-743.