A 24-year-old woman with no relevant past history visited our department with a lesion in the right lumbar region; the lesion had appeared 2 years earlier, had increased in size in the past 6 months, and had become painful on rubbing.
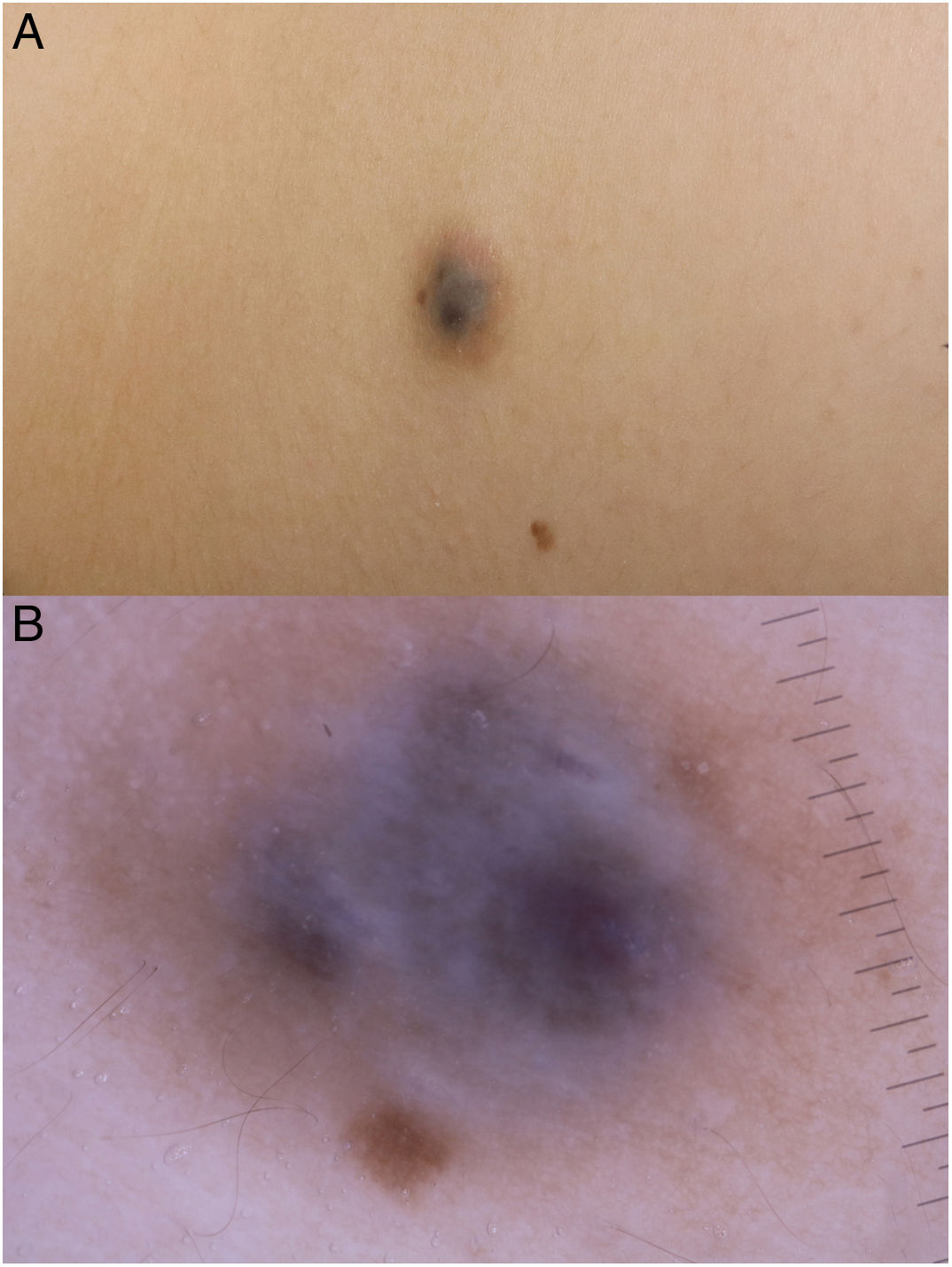
Physical examination revealed a bluish nodule measuring 1.5 × 1.5 cm, surrounded by a brown halo, with no thrill, pulse, or increase in local temperature (Fig. 1A).
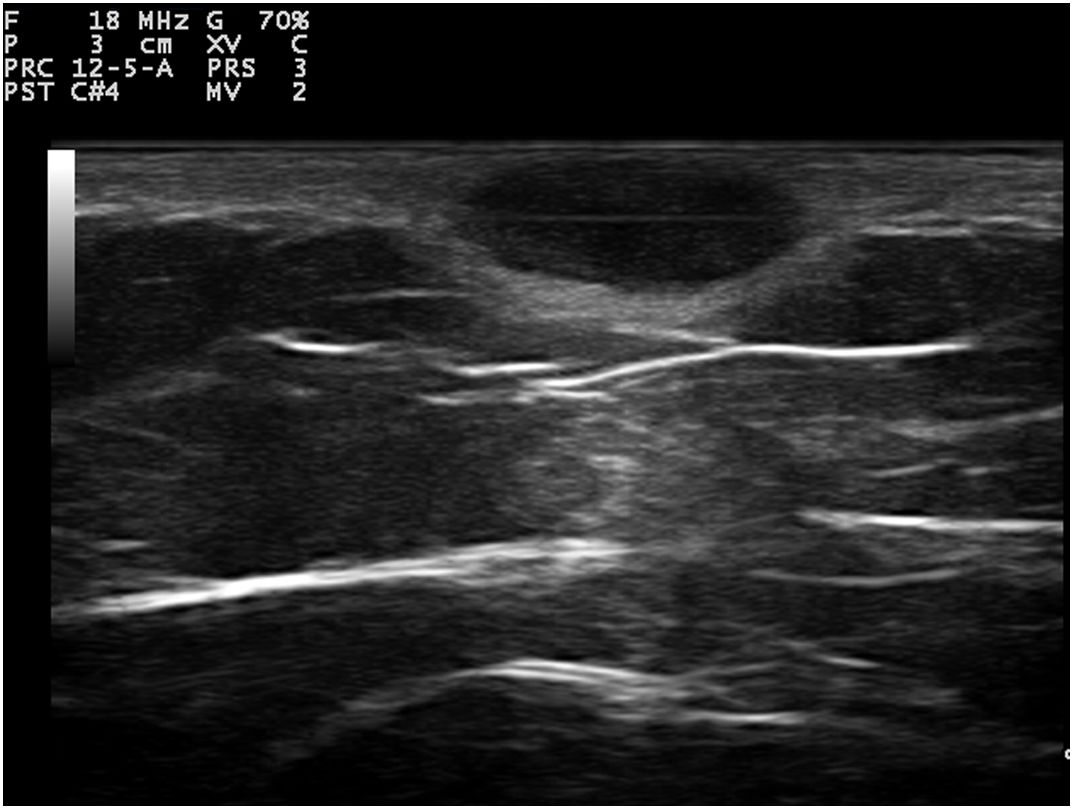
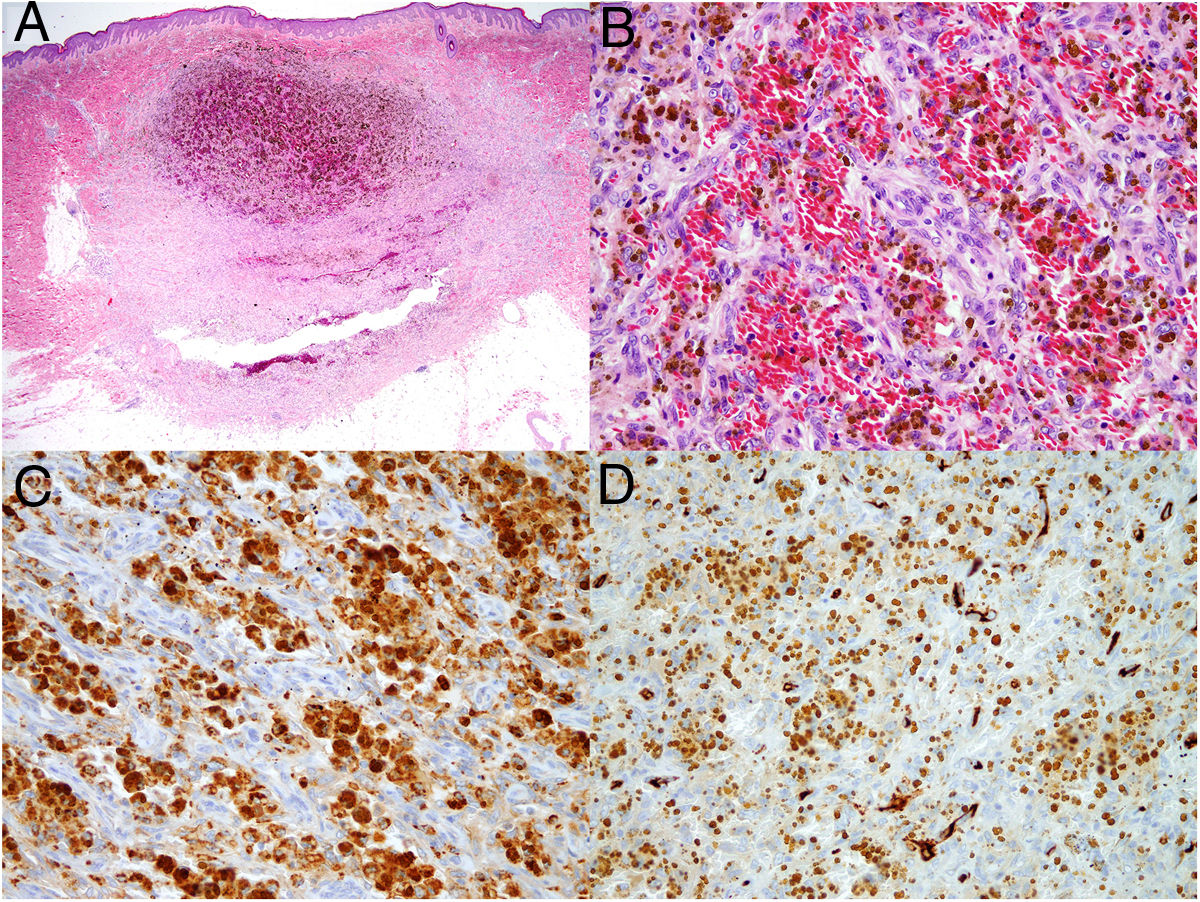
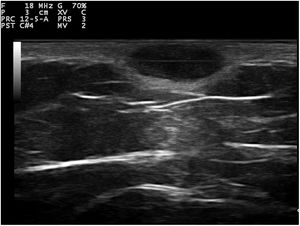
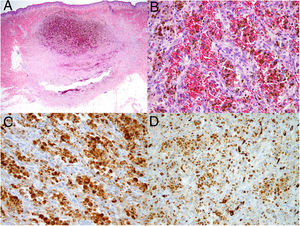
Dermoscopy revealed a uniform blue-violaceous background with no vascular structures in the interior, surrounded by a monomorphic fine pigmented reticulum (Fig. 1B). The ultrasound study revealed a subcutaneous tumor consisting of hypoechogenic areas (Fig. 2) and presenting no flow in Doppler color mode. The lesion was excised with possible suspected diagnoses of aneurysmatic dermatofibroma, microvenular hemangioma, combined nevus, and melanoma. Histology revealed a dermal nodule consisting of a proliferation of histiocytes with the presence of multiple capillaries and hemosiderophages, and bands of collagen in the periphery (Fig. 3A). The study also revealed ectasias and channels with no endothelial coating, with extravasated red blood cells and hemosiderin (Fig. 3B). Immune staining was positive for CD68 (Fig. 3C) and factor XIII, and negative for CD31, CD34 (Fig. 3D), and S100.
[[?]]What is your Diagnosis?
DiagnosisAneurysmatic dermatofibroma.
Aneurysmatic dermatofibroma (ADF) is a rare variant of dermatofibroma and accounts for less than 2% of these tumors. It generally presents as a single violaceous, brown or blackish lesion of a larger size than is usual, located on the torso or the extremities of young people. The recurrence rate following resection is 2%. The differential diagnosis includes other benign tumors such as hemangiomas and malignant tumors such as Kaposi sarcoma, melanoma, angiomatoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma, or skin metastases.1 Dermoscopy examinations have found a uniform bluish background with no vascular structures, surrounded by a monomorphic fine pigmented reticulum.2
Ultrasound tends to show dermatofibromas as poorly defined hypoechoic areas that distort and amplify the hair follicles, which contain no calcium deposits. Under Doppler color, they tend to be hypovascular, although they may show thin arterial and venous vessels with a slow flow. Ultrasound of ADF has reported anechoic areas with no flow in Doppler color, which would correspond histologically to areas of hemorrhage. Areas of flow may also be found that would be related to vascular and cellular areas of the tumor.3–5
Confocal microscopy (CM) is a noninvasive diagnostic technique that makes it possible to study localized lesions down to the papillary dermis. Under CM, ADF reveals spaces circumscribed by areas of variable reflectance, described as a shoal-like image.6
In terms of histology, ADF shows a proliferation of fibrohistiocytic cells distributed in a storiform pattern and with areas of ectasis filled with red blood cells or hemosiderin, but which do not constitute true vascular structures, as they are negative for endothelial markers CD31 and CD34. The markers CD68 and FVIII are positive and S100 is negative, which makes it possible to differentiate the entity from other tumors such as Kaposi sarcoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, melanoma, and some neural tumors. According to the cases reported in the literature, this is a tumor with a high rate of recurrence, close to 2% after incomplete resection. For this reason, treatment with Mohs surgery has also been tried.5 Our patient remains asymptomatic and free from recurrence after 1 year of follow-up.
In conclusion, both dermoscopy and ultrasound are harmless tests that help with the differential diagnosis of the subcutaneous nodules. More studies of this rare variant of dermatofibroma are required that make it possible to define its diagnostic criteria from a clinical, dermoscopic, and radiologic perspective. Meanwhile, suspected ADF must be resected, as only histology makes it possible to reach a diagnosis with certainty.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Please cite this article as: Giacaman A, Martínez MA, del Pozo Hernando LJ. Nódulo lumbar en una mujer joven. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ad.2019.01.025