Kindler syndrome is a very rare form of bullous epidermolysis. It is a hereditary condition caused by a mutation in the FERMT1 gene that encodes the protein kindlin-1. It is clinically characterized by trauma-induced blistering, diffuse skin atrophy, poikiloderma, pseudosyndactylyl, and photosensitivity. The most common mucosal manifestations are conjunctivitis, ectropion, hemorrhagic gingivitis, periodontal disease, premature tooth loss, and severe colitis. We present the first 4 cases of Kindler syndrome diagnosed at the Instituto Nacional de Salud del Niño in Lima, Peru. These cases highlight the unique clinical presentation and multiple manifestations of this disease and show how a multidisciplinary management approach kept symptoms under control and significantly improved patient quality of life.
El Síndrome de Kindler, es un subtipo de epidermólisis bullosa hereditaria muy rara, causada por la mutación del gen FERMT1 que codifica la proteína kindlina1.
Clínicamente se caracteriza por la formación de ampollas inducidas por trauma, atrofia cutánea difusa, poiquilodermia, pseudosindactilia y fotosensibilidad. En mucosas las manifestaciones mas frecuentes incluyen conjuntivitis, ectropión, gingivitis hemorrágicas, enfermedad periodontal, pérdida prematura de dientes y colitis severa.
Presentamos los 4 primeros casos con Síndrome de Kindler, diagnosticados en el Instituto Nacional de Salud del Niño Lima-Perú; con el fin de dar a conocer su particular forma de presentación y variedad de manifestaciones clínicas, enfatizando en que este hecho obligó a realizar un manejo multidisciplinario, que permitió un control adecuado de los síntomas y una notable mejoría en su calidad de vida.
Kindler syndrome (KS) is an autosomal recessive genodermatosis first described by Kindler in 1954.1
It is a rare subtype of hereditary epidermolysis bullosa (EB).2 Only 250 cases have been reported worldwide.3 In Peru it accounts for 4.3% of EB cases, according to a report that includes all 4 cases presented in this article.4
KS is caused by a mutation in FERMT1, the gene that encodes kindlin-1 protein, which is expressed in the skin, periodontal tissue, small intestine, colon, and rectum.5,6 Kindlin-1 forms part of the cytoskeleton of basal keratinocytes, and participates in cell migration, adhesion, and growth.5,7 Loss of kindlin-1 function results in skin fragility and defective binding of actin to the extracellular matrix.8
Clinical manifestations usually present from birth and consist of blistering induced by trauma or sun exposure, diffuse skin atrophy, and early-onset poikiloderma in photo-exposed areas. Photosensitivity improves with age, but affected individuals are predisposed to malignant skin tumors in adulthood.1,5 Mucosal involvement usually begins in adolescence; the oral mucosa is the most affected,5,9 resulting in hemorrhagic gingivitis, periodontal disease, and premature tooth loss. Other manifestations include conjunctivitis; ectropion; esophageal, urethral, and anal stricture; and constipation and severe colitis.3
We present 4 cases of KS patients who underwent multidisciplinary management and achieved adequate control of symptoms and complications.
Case 1The patient was a 13-year-old boy who was born to consanguineous parents and was seen for fragility of the skin and mucous membranes that began at age 5 years with small erosions that formed on the hands and feet after minimal trauma, pain and bleeding of the gums, diarrhea, and intermittent constipation.
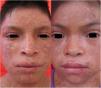
Physical examination revealed dry skin, areas of atrophic skin with a cigarette-paper-like appearance, sun-tan-like hyperpigmentation, and telangiectasias predominantly in photo-exposed areas, as well as pseudosyndactyly of the hands and punctate keratotic papules on the soles of the feet (Figs. 1 and 2).
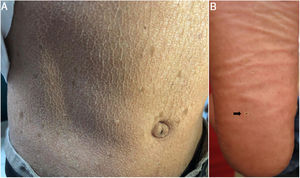
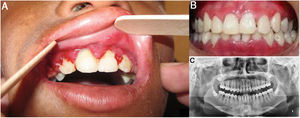
An ophthalmological examination revealed bilateral limitation of eye opening, amblyopia, and strabismus. A dental examination showed a reduction in mouth opening; dry lips with areas of hyperpigmentation; angular cheilitis; generalized stomatitis and poor oral hygiene; gingival hyperplasia (periodontal pockets and pseudo-pockets); bacterial plaque; dental calculus; grade 1 mobility in anterior teeth; and dental caries. Whitish, lichenoid-like lesions were observed on the palate (Fig. 3).
Dental evaluation of Case 1. A, Gingivitis, periodontitis, and gingival hyperplasia (periodontal pockets and pseudo-pockets), with bacterial plaque, dental calculus, and grade 1 mobility in anterior teeth. B, Post-treatment view of teeth in occlusion in which a marked clinical improvement is evident. C, Panoramic radiograph showing horizontal resorption of interdental crests.
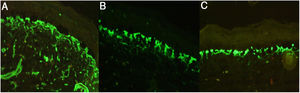
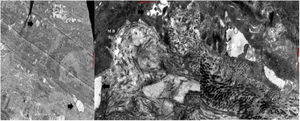
Immunofluorescence (IF) showed a reticular staining pattern for collagen IV, laminin 332, and collagen VII, and positive antikindlin-1 staining (Fig. 4).
Electron microscopy (EM) showed epidermal segments with normal keratinization and cleavage planes at different levels of the dermoepidermal junction, with the presence of desmosomes and anchoring fibrils (Fig. 5).
Permanent treatment with sunscreen and skin moisturizer was recommended. The patient underwent preventive, palliative, symptomatic, and recuperative dental treatment consisting of scaling and manual and ultrasonic curettage combined with dietary changes and nutritional supplementation for chronic malnutrition.
After 3 months, the patient’s skin condition and periodontal health improved considerably, and the periodontogram showed marked changes.
Case 2The patient was the 11-year-old brother of the patient in Case 1, and had skin lesions that were present from birth. In the 2 years preceding the consultation he experienced recurrent episodes of diarrhea alternating with constipation and encopresis, requiring use of a diaper. Physical examination revealed dry skin with atrophic areas, hyperpigmentation and poikiloderma on the face, neck, and chest, and pseudosyndactyly of the hands and feet (Fig. 1).
A dental examination revealed dry lips, dyschromia, angular cheilitis, and microstomia; gingival hyperplasia, bacterial plaque, and dental calculus in the upper teeth; and marked loss of bone support in the lower central and lateral incisors with grade 3 mobility. The patient was chronically malnourished and of short stature.
IF revealed a positive reticular staining pattern for collagen IV and VII and laminin 5, and positive antikindlin-1 staining. Blisters at various levels in the dermoepidermal junction were observed on EM. Barium X-ray of the colon showed dolichomegacolon.
Permanent treatment with sunscreen and skin moisturizer was recommended, as well as dental scaling and curettage. The gastroenterology department proposed treatment with osmotic laxatives and dietary changes for the management of colitis and encopresis, as well as nutritional supplementation.
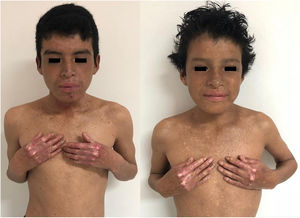
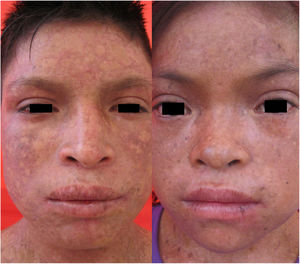
Case 3The patient was a 15-year-old boy from a small town in the Peruvian Amazon who was born to non-consanguineous parents. He was seen for blistering lesions that formed in response to minimal friction and had first appeared at 2 months of age. Physical examination revealed dyschromia and multiple lentigines in photo-exposed areas and on the labial mucosa; poikiloderma on the face, neck, and the dorsal aspects of the hands and feet; pseudosyndactyly; and plantar pitting (Figs. 2B and 6). The patient also presented gingival hypertrophy and dental caries.
IF revealed a positive reticular staining pattern for collagen IV and VII and laminin 332. EM showed blistering due to cytolysis in the basal layer, lamina lucida, and lamina densa, and the presence of anchor filaments and fibrils.
Treatment consisted of the use of sunscreen and moisturizers, dental scaling and curettage, and nutritional and psychological evaluation.
Case 4The patient was a 10-year-old girl, who was the sister of the patient in case 3. From the age of 6 months she presented bullous lesions that left dyschromic scars; skin atrophy; poikiloderma; and freckles predominantly in photo-exposed areas. She had pseudosyndactyly of the hands, gingival hypertrophy, and dental caries. The ophthalmological examination revealed conjunctivitis and mild bilateral ectropion of the lower eyelid (Fig. 6).
Clinical manifestations in Cases 3 and 4. Both patients presented with skin atrophy, hypochromic and hyperchromic areas with multiple telangiectasias (poikiloderma), and freckles predominantly in photo-exposed areas, as well as conjunctivitis and mild bilateral ectropion of the lower eyelid (right-hand image).
IF and EM revealed findings compatible with KS. Management of the patient included the permanent use of artificial tears and lenses with protection against ultraviolet A and B light.
DiscussionKS is an autosomal recessive condition.5 While most reported patients are descendants of consanguineous parents (Cases 1 and 2), KS can also occur as a result of spontaneous mutation.10 While the parents of Cases 3 and 4 denied kinship, they both come from small border towns. If we assume that the parents of the 4 cases described here are asymptomatic heterozygous carriers, the probability of each couple having a child with KS is 25% per pregnancy,3 hence the importance of providing patients and their parents with genetic counseling.
In KS, a mutation in the FERMT1 gene results in loss of function, leading to keratinocyte detachment, duplication of the lamina densa, and multiple cleavage planes at different levels of the dermoepidermal junction, beginning at birth.5,7 From the first years of life all 4 patients presented skin fragility that subsequently diminished, leaving patients with cutaneous atrophy and poikiloderma predominantly in photo-exposed areas. In addition, all 4 patients presented pseudosyndactyly that did not require surgical treatment as it did not compromise functionality.3 All patients presented plantar pitting.
Blistering and photosensitivity improve with age, while poikiloderma and skin atrophy persist.3 Around 10% of patients with KS can develop malignant skin tumors,1,11 such as squamous cell carcinoma, after 45 years of age.5 The mechanism underlying carcinogenesis may be related to low levels of transforming growth factor β and increased Wnt signaling, both of which have been described in humans and mice with KS.12,13 The use of sunscreen and protective clothing is essential to minimize the risk of carcinogenesis in these patients, especially in countries with high levels of solar radiation, such as Peru.3,13
Involvement of the mucosa, especially the oral mucosa (85%), is frequent; patients can present with periodontitis, gingival hyperplasia, premature tooth loss, caries, and halitosis,14 resulting in a vicious cycle of poor hygiene and periodontal disease. All 4 patients presented alterations in the oral mucosa, and received preventive, palliative, and recuperative treatment for chronically affected periodontal tissue. Treatment responses were favorable, but unstable and transitory. These patients should therefore continue to receive supportive periodontal therapy to improve oral hygiene.
Involvement of the ocular, esophageal, anal, and urogenital mucosa is more frequent after 10 years of age.5 The patient in Case 4 presented conjunctivitis and mild ectropion in the lower eyelid, which was managed by the ophthalmology department. Intestinal involvement in the form of colitis due to epitheliolysis (15%)5 is more severe in the complete absence of kindlin-1; intestinal kindlin-1 isoforms can compensate for partial kindlin-1 absence and therefore not all patients have digestive symptoms.6 In Cases 1 and 2, episodes of colitis were reported, associated in Case 2 with encopresis, which led to chronic malnutrition and short stature.
Diagnosis of KS is clinical, supported by IF findings showing an intense, widespread, cross-linked immunostaining pattern in the dermoepidermal membrane for laminin 332 and collagen types IV and VII.3,15,16 Positive immunostaining for antikindlin-1 is also considered diagnostic. Cleavage planes are a characteristic finding of this condition,18 and are visible on EM in intraepidermal, intralamina lucida, and sublamina densa regions.3,17 All previously described findings were observed in our 4 patients.
Diagnosis can be confirmed using molecular genetic techniques to verify mutation of FERMT.5,13 That this type of analysis was not feasible in our patients was one of the limitations of the study.
ConclusionKS is a subtype of EB that is very rarely reported in the medical literature. We present the first 4 cases reported in Peru and describe the specific presentations and associated clinical manifestations. We wish to emphasize the importance of managing these patients using a multidisciplinary approach in order to establish a timely diagnosis and to adequately control clinical signs and prevent complications, thereby improving patient prognosis and quality of life.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
The authors thank Drs. Roxana Lipa Chancolla, Luis Claudio Huamaní Huayhua, Gilmer Torres Ramos, and Rosario Loaiza de la Cruz.
Please cite this article as: Torres-Iberico R, Condori-Fernández Y, Apagüeño-Ruiz C, Andia-Ticona M, Pomar-Morante R. Síndrome de Kindler, manejo multidisciplinario. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ad.2019.04.013