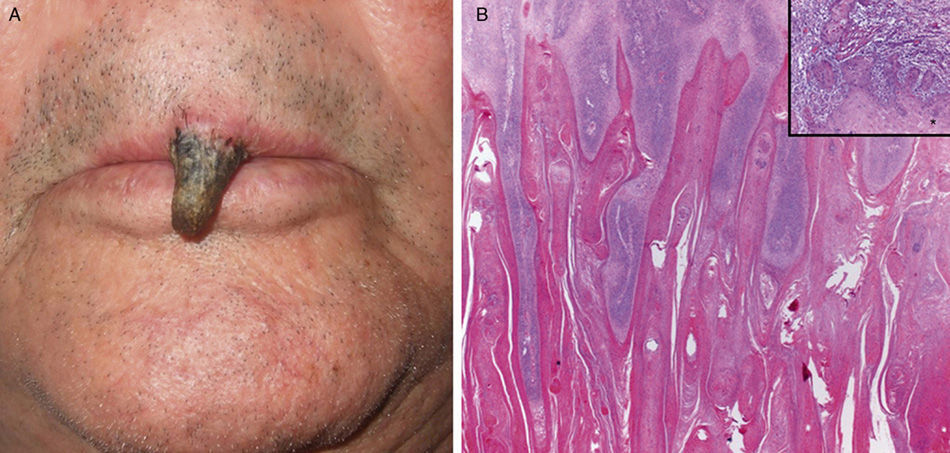
Our patient was a 66-year-old man who consulted for a horn-like exophytic lesion that had developed on his upper lip over a period of 8 months and interfered with eating. The patient was a rural laborer. He was a nonsmoker and did not drink alcohol. Dermatologic examination revealed a firm, hyperkeratotic brown mass measuring 3cm in length and 2cm in diameter, with its indurated base situated at the vermillion border of the upper lip (Fig. 1A). There were no palpable locoregional lymph nodes. Complete surgical excision of the lesion was performed and histology showed findings compatible with differentiated squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) on a cutaneous horn (Fig. 1B), with atypical epithelial cells with prominent nucleoli in the epidermis, forming nests that infiltrated the surrounding stroma (Fig. 1B, inset). No recurrence or metastases were detected during 2 years of follow-up.
The main risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma is chronic sun damage, and the tumor commonly arises in sun-exposed areas such as the face and lower lip; the upper lip is affected in only 2% to 12% of cases. Cutaneous horn is a hyperkeratotic tumor with a conical appearance. It is associated with various benign conditions (seborrheic keratosis, common warts) as well as premalignant (actinic keratosis) and malignant (SCC) lesions. If a malignant lesion is suspected, excision biopsy including the base of the lesion must be carried out to perform histologic examination. Adequate diagnosis and treatment of SCC of the lip is very important because of its metastatic potential.
Please cite this article as: Blasco-Morente G, Arias-Santiago S, Pérez-López I, Aneiros-Fernández J. Cuerno cutáneo en labio superior. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2016;107:429.